How Shaping Health Policy Can Secure Market Access
Market access is the key to success in the life science industry. A successful market access plan should include health policy-shaping strategies as well.
In this article, I would like to demonstrate how life science companies can actively shape and influence health policies to facilitate smoother market access. By leveraging policy-shaping strategies such as early engagement with regulatory bodies, providing robust evidence of product value, and collaborating with stakeholders like payers and healthcare providers, companies can enhance their chances of securing market access.
Through proactive efforts in policy-shaping, life sciences firms can align their innovations with national and international health priorities, ensuring better outcomes for both their products and patients.
The Role of Health Policy in the Life Sciences Sector
Health policy forms the backbone of how healthcare is delivered, funded, and regulated across the globe. For the life sciences sector, these policies dictate critical aspects such as drug approvals, medical device regulation, clinical trial standards, and reimbursement structures. Given the high stakes of bringing innovative therapies to market, understanding and navigating health policies is essential for companies operating in this space. A well-aligned strategy with health policy can accelerate product development, approval, and ultimately, access to patients.
Understanding Market Access and Its Relevance to Life Science Products
Market access refers to the process through which a life science product, such as a drug or medical device, becomes available to patients after passing regulatory scrutiny. This encompasses regulatory approval, pricing negotiations, and securing reimbursement from health systems or insurers. The success of any life science product is contingent upon gaining this market access, which is often influenced by the healthcare policies in place. Without proper access, even the most innovative products may struggle to reach patients in need.
Understanding Market Access in Life Sciences
Market access is a critical component of the life sciences industry, shaping the pathway by which innovative products such as drugs, medical devices, and biotechnology solutions reach the market and, more importantly, the patients who need them. It goes beyond mere regulatory approval, encompassing a broader framework that includes pricing, reimbursement, and value demonstration to healthcare systems.
Successful market access strategies ensure that life science products are not only approved by regulators but are also accessible and affordable for patients, with key stakeholders like government bodies, healthcare providers, payers, and patients playing essential roles in this process. In a landscape that is highly regulated and cost-sensitive, life science companies must carefully navigate these factors to achieve both commercial success and patient access.
Definition of Market Access for Life Science Products
Market access is a crucial process that determines whether life science products, such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and biotech innovations, can reach the patients who need them. In its simplest terms, market access refers to the ability of a product to be approved, reimbursed, and available within a healthcare system. For life science companies, market access is not just about obtaining regulatory approval but also ensuring that their products are accessible, affordable, and reimbursed by health systems and insurance providers. Without successful market access, even the most groundbreaking innovations may remain out of reach for patients due to financial, regulatory, or logistical barriers.
Market access strategies are multifaceted, covering aspects such as clinical trial outcomes, cost-effectiveness, health technology assessments (HTA), and negotiations on pricing and reimbursement with governments or payers. The complexity of gaining market access varies from country to country due to different health systems, policies, and regulations.
The Role of Regulatory Approval, Reimbursement, and Pricing
Regulatory approval, reimbursement, and pricing are the cornerstones of market access for life science products. These three elements work in tandem to determine whether a new drug, medical device, or biotech innovation can enter the market and be utilized by healthcare systems. Regulatory approval ensures the product meets safety, efficacy, and quality standards.
However, gaining approval is just the beginning. To reach patients, life science companies must secure reimbursement from payers, demonstrating that the product offers value for money and improves patient outcomes.
Pricing, often negotiated with government bodies and insurers, is equally critical as it directly affects affordability, access, and the product’s overall commercial success. Together, these elements form the foundation of a successful market access strategy.
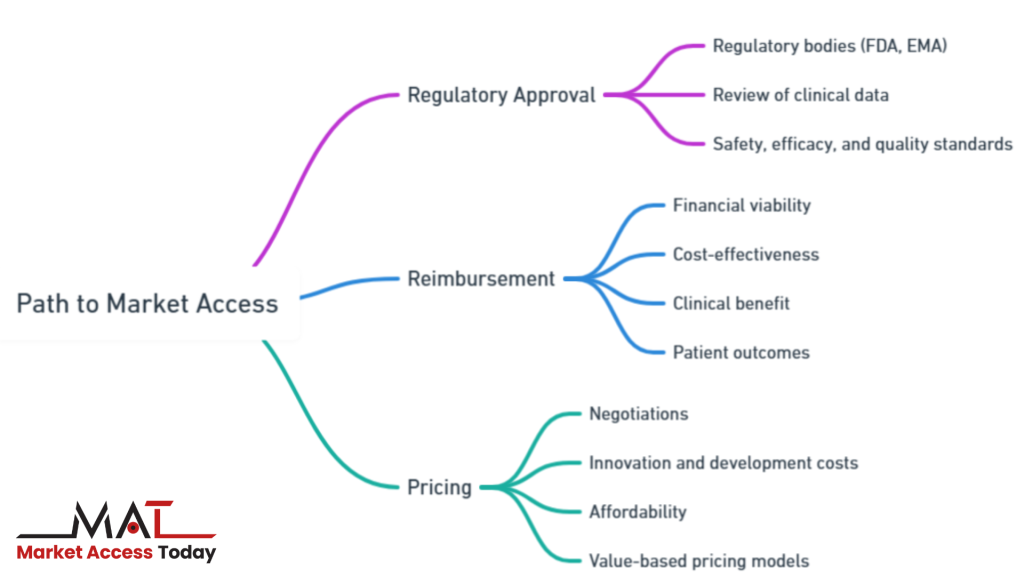
The path to market access involves several key steps:
- Regulatory Approval: Before any life science product can be made available to the public, it must go through rigorous regulatory approval processes, ensuring that it meets safety, efficacy, and quality standards. Different regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States or the EMA in Europe, review the clinical data to grant or deny approval. Obtaining regulatory approval is the first critical step toward market access.
- Reimbursement: Even after a product is approved, it must be reimbursed by healthcare systems or insurers to become financially viable for widespread use. Reimbursement is based on an assessment of the product’s value, which often includes its cost-effectiveness, clinical benefit, and impact on patient outcomes. Without reimbursement agreements, patients may be unable to afford the product, limiting its market penetration.
- Pricing: Negotiating pricing is another crucial factor in market access. Governments and payers seek to control healthcare costs, so price setting for life science products can involve complex negotiations. Companies must balance setting prices that reflect the innovation and development costs while ensuring affordability within healthcare systems. Value-based pricing models, where reimbursement is linked to the clinical outcomes of the product, are becoming increasingly popular.
Key Stakeholders in Market Access
Securing market access for life science products requires the involvement and collaboration of several key stakeholders, each playing a pivotal role in determining whether a product can reach patients.
Government bodies and regulatory agencies set the rules for product approval and, in many cases, influence pricing and reimbursement decisions. Healthcare providers, such as physicians and hospitals, are responsible for recommending and administering treatments, making their acceptance of new products essential for success. Payers and insurers assess the value and cost-effectiveness of a product, deciding whether it will be reimbursed and at what level.
Finally, patients and patient advocacy groups are increasingly influencing access decisions, advocating for timely approval and availability of innovative treatments. Engaging with these stakeholders early and effectively is crucial for navigating the complexities of market access and ensuring that life science products can fulfill their potential to improve patient outcomes.
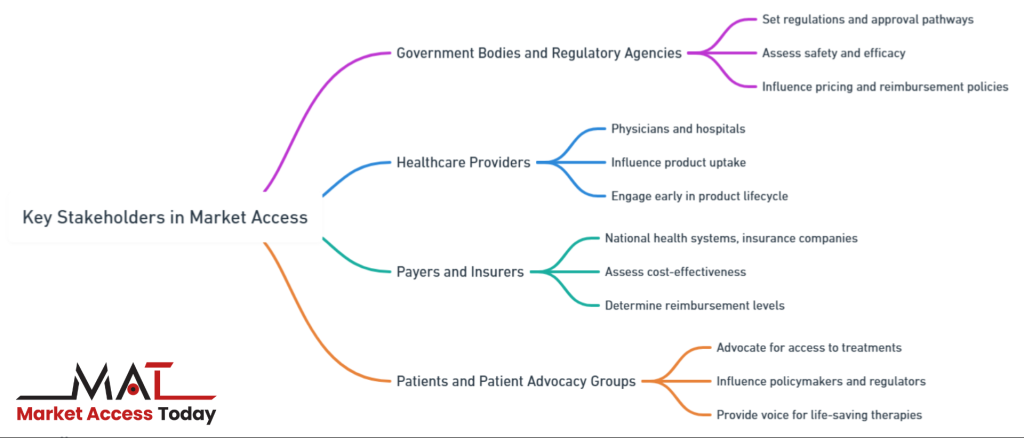
Several key stakeholders play pivotal roles in determining market access:
- Government Bodies and Regulatory Agencies: These entities set the regulations and approval pathways for life science products. They assess safety and efficacy through clinical trials and grant approval for market entry. In many cases, they also play a role in price-setting and reimbursement policies, making their engagement critical to the success of market access strategies.
- Healthcare Providers: Physicians, hospitals, and healthcare organizations influence product uptake by deciding which treatments to offer to patients. Engaging with healthcare providers early in the product lifecycle can help life science companies understand clinical needs, improve product adoption, and demonstrate real-world effectiveness.
- Payers and Insurers: Payers, such as national health systems, insurance companies, or managed care organizations, determine whether a product will be reimbursed and at what rate. Payers require robust evidence of the product’s cost-effectiveness and impact on patient outcomes to justify reimbursement. Negotiating favorable reimbursement terms is often a key driver of successful market access.
- Patients and Patient Advocacy Groups: Patients are increasingly influential in market access decisions, particularly when it comes to advocating for access to new treatments. Patient advocacy groups can provide a voice for those in need of life-saving therapies and can influence policymakers and regulators to expedite approval or reimbursement decisions.
By engaging with these stakeholders, life science companies can better navigate the complexities of market access, ensuring that their products meet regulatory requirements, achieve favorable pricing and reimbursement outcomes, and ultimately, reach the patients who need them.
Health Policy as a Tool for Market Access
Health policy plays a critical role in shaping the market access landscape for life science products. By aligning with existing health policies, life science companies can more effectively navigate regulatory hurdles, secure favorable pricing, and achieve reimbursement.
Changes in health policy can significantly impact pricing models, distribution strategies, and reimbursement processes, often requiring companies to demonstrate cost-effectiveness and clinical value through mechanisms like Health Technology Assessments (HTAs). Policies around reimbursement guidelines and pricing frameworks, such as value-based pricing, also directly influence whether a product can enter the market successfully.
Understanding and leveraging these health policies is essential for life science companies to ensure their products are not only approved but also accessible and affordable to patients. By actively engaging with policymakers and aligning product development strategies with national health priorities, companies can use health policy as a powerful tool to secure and sustain market access.

Importance of Aligning with Health Policies to Achieve Successful Market Entry
Health policy plays a fundamental role in determining whether life science products can successfully enter and thrive in a particular market. Aligning with these policies is essential for life science companies as they navigate the regulatory landscape to bring their products to patients. Policies around drug approvals, medical device regulation, and pricing shape the pathway for market access.
By proactively aligning product development strategies with existing and evolving health policies, companies can not only speed up market entry but also enhance their chances of long-term success. This alignment involves understanding national health priorities, such as cost containment, public health needs, and innovation incentives, ensuring that the product fits within the healthcare system’s goals.
The Impact of Health Policy Changes on Pricing, Reimbursement, and Distribution
Health policy changes can have a significant impact on how life science products are priced, reimbursed, and distributed. Governments and regulatory bodies often implement policy changes to control healthcare spending, promote generic medicines, or encourage value-based healthcare. These changes can lead to adjustments in the reimbursement processes, pricing regulations, and distribution models that life science companies must adhere to.
For example, price-setting policies may limit the profitability of innovative drugs, while new reimbursement criteria may require companies to demonstrate cost-effectiveness through health technology assessments (HTAs). Policy shifts toward decentralized healthcare models can also alter how products are distributed, pushing companies to rethink their strategies for market entry and distribution logistics.
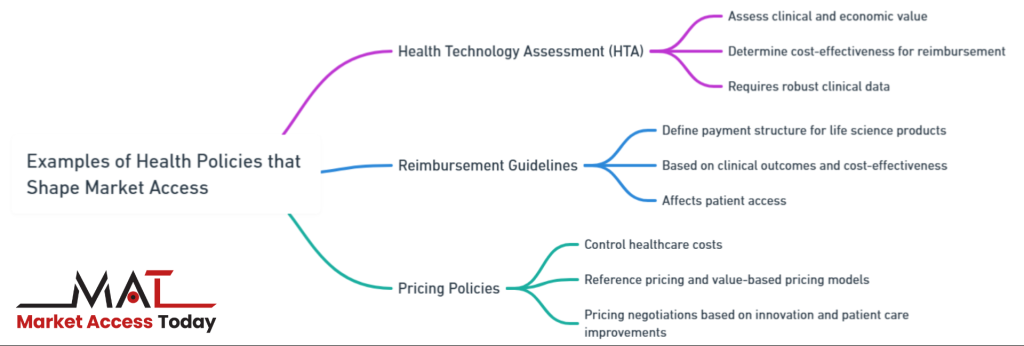
Examples of Health Policies that Shape Market Access
Several specific health policies directly influence the ability of life science products to gain market access:
- Health Technology Assessment (HTA): HTA is a critical policy tool used by many countries to assess the clinical and economic value of new medical products. Through HTA processes, government bodies evaluate whether a product is cost-effective and provides enough clinical benefit to warrant reimbursement. Life science companies must prepare robust data on their product’s effectiveness, safety, and cost-effectiveness to meet HTA criteria.
- Reimbursement Guidelines: Reimbursement policies determine whether and how much a healthcare system will pay for a life science product. These guidelines are based on factors like clinical outcomes, cost-effectiveness, and comparative benefits over existing treatments. Companies must work within these frameworks to ensure their products receive favorable reimbursement terms, as lack of reimbursement often limits patient access.
- Pricing Policies: Governments frequently implement pricing policies aimed at controlling healthcare costs, particularly for pharmaceuticals. These policies can include reference pricing, where the price of a drug is compared to prices in other countries, or value-based pricing models that tie the price of a product to its clinical outcomes. Life science companies must engage with policymakers and payers to negotiate prices that reflect both the product’s innovation and its potential for improving patient care.
In summary, health policy serves as a powerful tool for shaping market access. By understanding and aligning with health policy changes, life science companies can effectively navigate the regulatory landscape, optimize pricing and reimbursement, and ensure their products are distributed to the patients who need them.
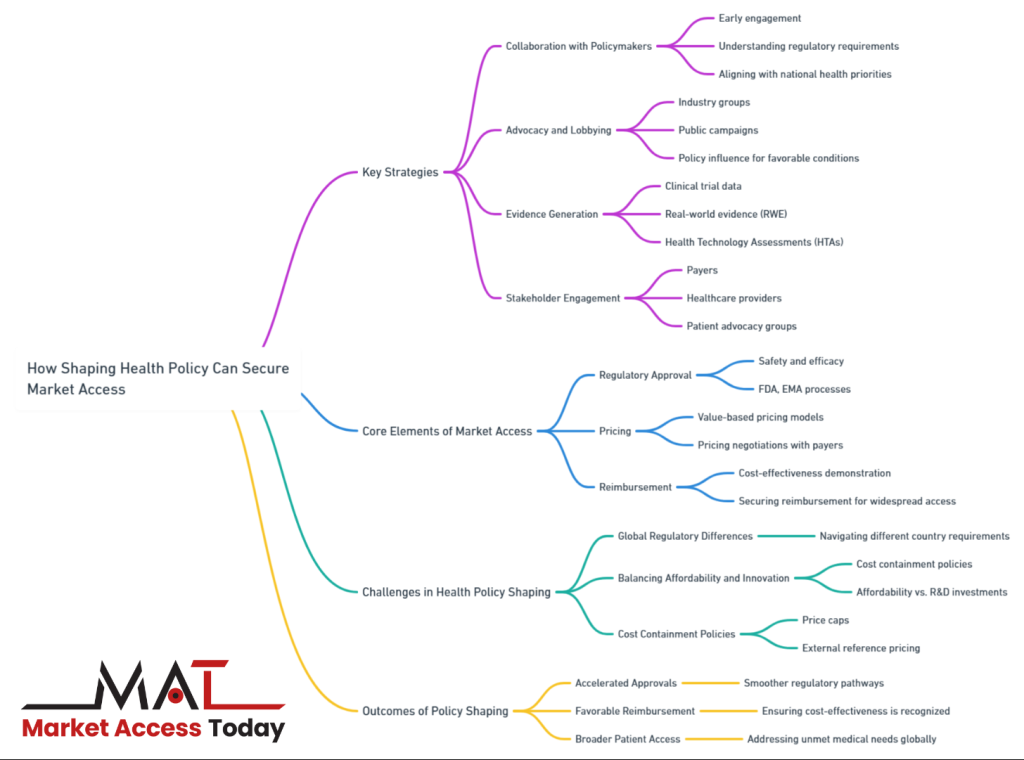
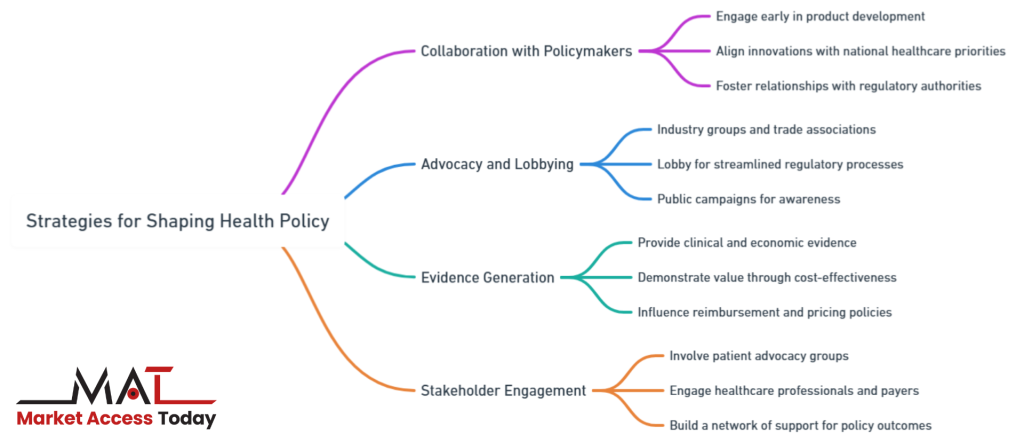
Strategies for Shaping Health Policy
Shaping health policy is essential for life science companies seeking to secure market access for their products. A proactive approach to influencing policy can streamline regulatory approvals, improve reimbursement terms, and ensure that innovative treatments reach patients more quickly.
This process requires a multi-faceted strategy, involving early collaboration with policymakers, robust advocacy and lobbying efforts, and the generation of strong clinical and economic evidence to demonstrate product value. Additionally, engaging with key stakeholders such as patient advocacy groups, healthcare professionals, and payers plays a pivotal role in building a supportive network that can influence favorable policy decisions.
Together, these strategies help life science companies navigate the complex policy environment and maximize their chances of successful market access.
Collaboration with Policymakers
One of the most effective strategies for shaping health policy is engaging with policymakers and regulatory bodies early in the product development process. This early collaboration allows life science companies to align their innovations with the evolving priorities of national healthcare systems, ensuring smoother market access.
By fostering relationships with government agencies and regulatory authorities, companies can better understand the policy landscape, anticipate upcoming changes, and adapt their strategies accordingly. Regular communication and transparency with policymakers also help companies position their products as valuable solutions that address public health needs, which can influence favorable policy outcomes related to approval, reimbursement, and distribution.
Advocacy and Lobbying
Advocacy and lobbying are crucial tools in the policy-shaping arsenal. Industry groups, trade associations, and professional organizations can lobby for policies that benefit the life sciences sector, including streamlined regulatory processes, favorable reimbursement frameworks, and incentives for innovation. Through lobbying efforts, companies can advocate for changes in healthcare policy that remove barriers to market access or provide incentives for new therapies and technologies.
Successful lobbying campaigns often involve creating compelling narratives about how specific policies impact patient care and public health, thus persuading legislators to enact changes that favor market access for life science products. Furthermore, advocacy can take the form of public campaigns that raise awareness about unmet medical needs or the societal benefits of new treatments, thereby pressuring governments to adjust health policies accordingly.
Evidence Generation
Providing robust clinical and economic evidence is a cornerstone of any successful health policy-shaping strategy. Governments, payers, and regulatory bodies require comprehensive data on the safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness of life science products before granting approval or reimbursement.
Companies can influence health policy by generating high-quality evidence that demonstrates the value of their products. This includes clinical trial data, real-world evidence, and health economic studies that show how the product improves patient outcomes while also being cost-effective for healthcare systems.
Evidence that demonstrates a product’s ability to reduce long-term healthcare costs or improve quality of life can be particularly influential in shaping policies that affect reimbursement and pricing. Additionally, companies can leverage this evidence in health technology assessments (HTAs) and value-based pricing negotiations.
Stakeholder Engagement
Another key strategy in shaping health policy is engaging with a broad coalition of stakeholders, including patient advocacy groups, healthcare professionals, and payers. By involving these stakeholders early in the product development and market access process, companies can build a network of support that bolsters their case for favorable policy outcomes.
Patient advocacy groups, in particular, have gained significant influence in recent years by raising awareness about unmet medical needs and pushing for quicker access to innovative treatments. These groups can be powerful allies in persuading policymakers to prioritize certain products or therapeutic areas.
Similarly, engaging with healthcare providers and payers allows companies to gather valuable insights into clinical and payer priorities, helping them better tailor their products and strategies to meet market needs. Collaborative approaches that involve all stakeholders can enhance the credibility of a company’s policy-shaping efforts and increase the likelihood of achieving favorable market access conditions.
In summary, successfully shaping health policy requires a multifaceted approach. By collaborating with policymakers, engaging in advocacy and lobbying efforts, generating robust evidence, and working closely with key stakeholders, life science companies can effectively influence the policies that determine market access, pricing, and reimbursement for their products.
Case Studies of Successful Policy-Shaping
Real-world examples of companies that have successfully shaped health policy highlight the importance of strategic engagement with regulators, policymakers, and healthcare stakeholders. These case studies provide valuable insights into how aligning with national health priorities, generating robust evidence, and engaging early with decision-makers can facilitate smoother market access.
By taking a proactive approach to influencing health policy, companies can not only secure regulatory approvals and favorable reimbursement terms but also strengthen their position in the market. The following case studies illustrate how effective policy shaping can lead to significant success in securing market access for life science products.
Example 1: Securing Reimbursement through HTA by Aligning with National Health Priorities
A multinational pharmaceutical company sought to launch an innovative oncology drug, designed to treat a rare form of cancer, in a European market. The company recognized that securing market access for such a high-cost drug would be challenging, given the country’s stringent reimbursement policies and health technology assessment (HTA) requirements. To address these challenges, the company focused on aligning its product with the nation’s health priorities, which included improving cancer survival rates and reducing the financial burden of chronic diseases on the healthcare system.
Before initiating the HTA process, the company engaged with national health authorities and policymakers to understand the government’s long-term goals for cancer treatment. By demonstrating how the new oncology drug could contribute to achieving those objectives, particularly in terms of improving survival rates and reducing the need for more costly interventions in later stages of the disease, the company strengthened its case. The company also invested in generating compelling clinical and economic evidence, showing that the drug’s cost, though initially high, would result in long-term savings for the healthcare system by improving patient outcomes and reducing hospitalizations.
As a result of this targeted policy alignment and evidence generation, the HTA body recommended the drug for reimbursement, highlighting its potential to meet national health priorities. The company secured reimbursement at a price that reflected both the drug’s clinical value and the long-term economic benefits it offered. This example illustrates how aligning a product with national health priorities and leveraging robust evidence can result in successful market access and reimbursement.
Example 2: Proactive Engagement with Policymakers for Smoother Regulatory Approvals and Pricing Negotiations
A global biotechnology company was in the process of launching a novel biologic therapy for a chronic autoimmune condition in the U.S. market. Understanding the complexity of the U.S. healthcare system and the evolving policies around biologics, the company decided to engage with policymakers and regulatory agencies early in the product development process. By doing so, they aimed to streamline the regulatory approval process and secure more favorable pricing and reimbursement terms.
The company initiated early dialogues with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), providing them with clinical trial data as the studies progressed. These early discussions allowed the company to gather feedback on regulatory expectations, adapt their clinical trials to meet the FDA’s requirements, and anticipate challenges related to pricing and reimbursement. Additionally, the company collaborated with key congressional committees and participated in public forums discussing the future of biologic therapies and biosimilars, emphasizing the therapy’s potential to address unmet medical needs.
This proactive engagement paid off. By the time the product reached the FDA for approval, the agency was already familiar with its clinical profile and strategic importance in addressing chronic autoimmune conditions. As a result, the approval process was expedited. Furthermore, the company’s early involvement in pricing discussions with CMS helped secure a value-based pricing agreement that linked the product’s price to patient outcomes, making it more attractive to payers and increasing its potential market share.
This case highlights how early and proactive engagement with regulators and policymakers can not only smooth the regulatory approval process but also lead to better pricing and reimbursement outcomes. By building relationships and aligning product goals with broader health policy objectives, companies can shape policies in ways that facilitate successful market entry and access.
These examples demonstrate that a well-planned policy-shaping strategy that focuses on early engagement, strong evidence generation, and alignment with health priorities can significantly improve market access outcomes for life science products.
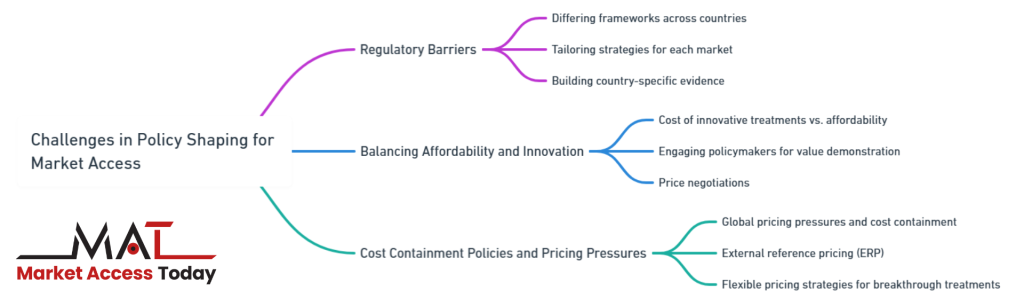
Challenges in Policy Shaping for Market Access
In the life sciences sector, shaping health policy to secure market access is often a complex and demanding process. While successful policy shaping can lead to faster regulatory approvals, better reimbursement terms, and broader patient access, there are significant challenges that life science companies must navigate. These challenges stem from regulatory differences between countries, the need to balance the affordability of innovative treatments, and the growing pressure from cost containment policies.
Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential for companies looking to achieve sustainable market access. The following section explores the key obstacles in shaping health policy for life science products and the strategies needed to overcome them.
Regulatory Barriers and Differing Health Policy Frameworks Across Countries
One of the most significant challenges in shaping health policy is the wide variation in regulatory frameworks and health policies across different countries. Each country has its own set of regulations, approval processes, and reimbursement criteria, making it difficult for life science companies to develop a one-size-fits-all approach.
For instance, while a product may gain approval and reimbursement in one country, the same product might face delays or rejection in another due to differing health priorities, clinical requirements, or economic evaluations. Additionally, varying degrees of regulatory stringency can create barriers to market entry, particularly in countries with complex health technology assessment (HTA) processes or lengthy approval timelines.
Companies must navigate these differences by tailoring their policy-shaping strategies to meet the specific regulatory and health policy requirements of each target market. This often involves building country-specific evidence and engaging with local regulatory bodies and stakeholders to ensure alignment with national priorities. Failing to do so can result in significant delays or market exclusion, limiting the product’s global reach and commercial success.
The Need for Balancing Affordability and Innovation
Another critical challenge in shaping health policy is the need to balance the cost of innovative treatments with affordability. Governments and payers are under increasing pressure to contain healthcare costs, while life science companies are focused on recovering the substantial investments made in research and development (R&D). This creates a tension between offering innovative, high-cost therapies and ensuring these treatments remain accessible and affordable to healthcare systems and patients.
Health policymakers often implement strict cost-containment measures, such as reference pricing, price caps, or value-based pricing models, to manage the rising costs of new therapies. For companies, this means they must provide compelling evidence that their product delivers sufficient value in terms of improved patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, or long-term economic benefits.
However, demonstrating this value while keeping prices affordable can be difficult, particularly for highly innovative treatments that require significant investment in R&D. Companies must strategically engage with policymakers to negotiate pricing and reimbursement terms that reflect both the product’s value and the need for affordability.
Challenges Posed by Cost Containment Policies and Global Pricing Pressures
The increasing use of cost containment policies globally poses yet another challenge for life science companies. Governments around the world are implementing stringent pricing regulations to control healthcare expenditure, particularly for expensive drugs and medical devices. These policies, such as external reference pricing (ERP), force companies to align their pricing strategies across multiple countries, often leading to lower prices in markets with strict pricing controls. In turn, this can create downward pricing pressure globally, as payers in other markets seek to benchmark prices against lower-cost countries.
Furthermore, cost containment policies can limit a company’s ability to negotiate favorable pricing, particularly in high-demand markets, which may lead to reduced profitability. This is especially challenging for companies launching breakthrough treatments or therapies for rare diseases, where pricing needs to reflect the product’s unique value and the smaller patient population. To navigate these pressures, life science companies must develop flexible pricing strategies and engage in early, transparent discussions with payers to advocate for value-based pricing models that take into account clinical outcomes and the broader impact on healthcare systems.
In conclusion, while shaping health policy is essential for securing market access, life science companies face numerous challenges in this process. From navigating complex regulatory frameworks across countries to balancing innovation with affordability and managing the impact of global pricing pressures, companies must adopt tailored, proactive strategies to overcome these obstacles.
Successfully addressing these challenges is critical to ensuring that life science products not only reach the market but also provide sustainable access to patients worldwide.
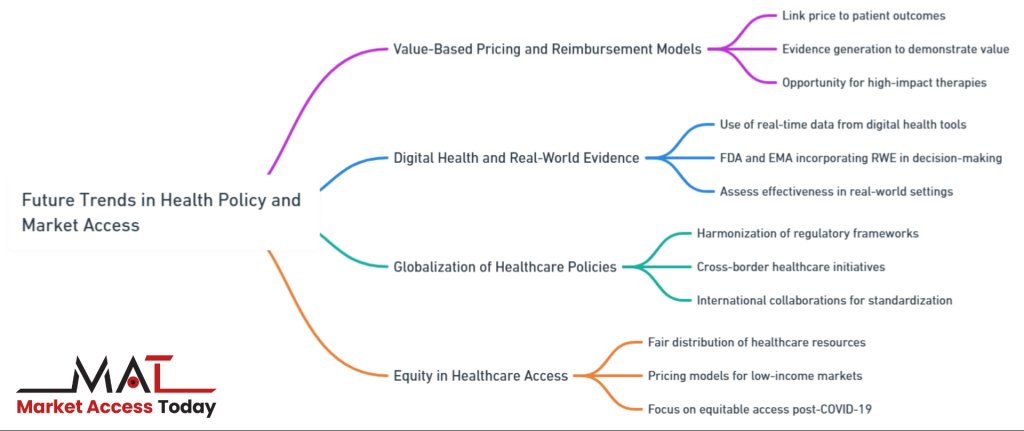
Future Trends in Health Policy and Market Access
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, new trends are emerging in health policy and market access that will shape the future of the life sciences industry. Companies must stay ahead of these trends to successfully navigate the changing environment and ensure their products can reach the market efficiently. Key developments include the increasing adoption of value-based pricing models, the growing importance of digital health and real-world evidence, the harmonization of regulations across borders, and a stronger focus on healthcare equity.
These trends represent both opportunities and challenges for life science companies, requiring proactive strategies to align with emerging policies and ensure sustainable market access. In this section, we explore these key future trends and discuss their implications for market access strategies.
Increasing Role of Value-Based Pricing and Outcomes-Based Reimbursement Models
One of the most significant shifts in health policy is the growing emphasis on value-based pricing and outcomes-based reimbursement models. Governments and payers are increasingly moving away from traditional pricing models that focus on the cost of production, and instead adopting value-based approaches that link the price of a product to the outcomes it delivers for patients. This shift is driven by the need to contain healthcare costs while ensuring that patients have access to innovative treatments that provide tangible clinical benefits.
In value-based pricing models, the reimbursement of a product is tied to its ability to deliver measurable improvements in patient outcomes, such as reduced hospitalizations or enhanced quality of life. These models are particularly relevant for expensive, high-impact therapies, such as gene therapies or cancer immunotherapies, where demonstrating value is critical to securing market access.
For life science companies, this trend means that evidence generation is becoming increasingly important. Companies must provide robust clinical data and real-world evidence to demonstrate that their products deliver value not only in clinical trials but also in everyday healthcare settings. This shift to value-based pricing represents a significant opportunity for companies that can prove the effectiveness and long-term value of their products.
The Impact of Digital Health and Real-World Evidence on Policy and Market Access Strategies
Digital health technologies and the use of real-world evidence (RWE) are transforming the way health policy is shaped and how market access strategies are developed. Digital health tools, such as wearable devices, telemedicine platforms, and health apps, generate vast amounts of real-time data that can be used to assess the effectiveness of treatments in real-world settings. This data offers new opportunities for life science companies to build a stronger case for market access by providing real-world evidence that supplements traditional clinical trial data.
Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly incorporating RWE into their decision-making processes, recognizing its potential to provide insights into how products perform outside of controlled clinical environments. For example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has been actively exploring the use of RWE in regulatory approvals, particularly for post-market surveillance and outcomes-based reimbursement models.
Similarly, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) is integrating digital health data into its regulatory framework. Life science companies must embrace digital health and RWE to align with these emerging policy trends and to ensure that their products meet the evolving standards of regulators and payers.
Globalization of Healthcare Policies: Harmonization of Regulations and Cross-Border Healthcare Initiatives
As the global healthcare market expands, there is a growing movement toward the harmonization of healthcare policies and regulatory frameworks across countries. This globalization of healthcare policy aims to create more consistent and streamlined regulations, reducing the barriers to market access for life science products. International collaborations, such as the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH), are working to standardize regulatory requirements for drug approvals, clinical trials, and safety monitoring across regions.
For life science companies, the harmonization of regulations presents significant opportunities to reduce the time and cost associated with bringing products to market in multiple countries. By aligning regulatory requirements, companies can conduct multinational clinical trials, submit unified regulatory filings, and reduce the duplication of compliance efforts.
In addition to harmonization, cross-border healthcare initiatives, such as joint procurement agreements and collaborative health technology assessments (HTAs), are emerging as important tools for expanding access to innovative therapies. However, while globalization offers many benefits, it also requires companies to navigate complex international relationships and adapt their market access strategies to meet the needs of diverse healthcare systems.
Equity in Healthcare Access
A growing focus on equity in healthcare access is emerging as a critical trend in health policy shaping and market access strategies. Equity in healthcare refers to the fair distribution of healthcare resources and access to treatments, ensuring that all individuals—regardless of socioeconomic status, geographic location, or demographics—can benefit from medical innovations. The COVID-19 pandemic has spotlighted global disparities in healthcare access, driving policymakers and life science companies to prioritize more equitable distribution of treatments and therapies.
For life science companies, this shift toward equity poses both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, demonstrating a commitment to equity by developing pricing models that consider low- and middle-income markets, or expanding access to underserved populations, can improve a company’s reputation and strengthen its relationships with governments and healthcare organizations.
On the other hand, the need for equitable access may require companies to rethink their market access strategies, particularly in terms of pricing and reimbursement. Balancing the need to recover R&D investments while making products affordable for disadvantaged populations is a complex challenge. Companies must work closely with policymakers to develop innovative approaches, such as tiered pricing models or expanded access programs, that promote equity without compromising financial sustainability.
The future of health policy and market access is shaped by trends that demand flexibility and innovation from life science companies. The shift to value-based pricing and outcomes-based reimbursement, the increasing reliance on digital health and real-world evidence, the globalization of healthcare policies, and the rising focus on equity all represent important developments that will redefine the landscape of healthcare access.
To succeed in this evolving environment, companies must embrace these trends, invest in evidence generation, engage with global regulatory bodies, and develop innovative strategies that balance commercial success with broader healthcare goals.
By doing so, they can secure sustainable market access for their products while contributing to a more equitable and effective healthcare system.
10 FAQs from “Health Policy Shaping to Secure Market Access for Life Science Products”:
1. What is market access in the life sciences industry?
Market access refers to the process by which a life science product (such as a drug or medical device) gains regulatory approval, secures reimbursement, and becomes accessible to patients within healthcare systems. It involves navigating pricing, reimbursement, and regulatory frameworks to ensure the product is affordable and available.
2. Why is shaping health policy important for market access?
Shaping health policy helps life science companies align their products with national healthcare priorities, facilitating faster regulatory approvals, better pricing terms, and broader reimbursement. By influencing policy, companies can improve their chances of achieving market access and commercial success.
3. What role does value-based pricing play in market access?
Value-based pricing ties the price of a product to the outcomes it delivers for patients. It’s increasingly used by governments and payers to ensure that new treatments are both clinically effective and cost-efficient, making it a critical element in securing market access.
4. How can early engagement with policymakers benefit life science companies?
Engaging with policymakers early in the product development process allows companies to anticipate regulatory changes, adapt to health policy requirements, and shape favorable market access conditions. It also helps companies align their innovations with national health priorities.
5. What is the importance of evidence generation for market access?
Generating robust clinical and economic evidence is crucial for demonstrating a product’s value to regulators, payers, and healthcare providers. Strong evidence, including real-world data, helps secure regulatory approval, favorable reimbursement, and product adoption in the market.
6. Who are the key stakeholders involved in market access?
Key stakeholders in market access include government regulatory bodies, healthcare providers, payers (such as national health systems and insurers), and patient advocacy groups. Collaborating with these stakeholders is essential for navigating market access challenges.
7. What challenges do life science companies face in shaping health policy?
Companies face challenges such as regulatory variations across countries, balancing the cost of innovation with affordability, and dealing with global pricing pressures. These challenges require tailored strategies to align with diverse regulatory frameworks and healthcare priorities.
8. How does health policy influence pricing and reimbursement?
Health policy directly impacts how life science products are priced and reimbursed. Policies such as health technology assessments (HTAs), reference pricing, and value-based pricing models determine whether a product is considered cost-effective and eligible for reimbursement by healthcare systems.
9. What trends are shaping the future of health policy and market access?
Key trends include the rise of value-based pricing, the increasing use of digital health and real-world evidence in regulatory decisions, the globalization of healthcare regulations, and a growing focus on equitable access to healthcare, especially for disadvantaged populations.
10. How can life science companies proactively shape health policy for successful market access?
Life science companies can proactively shape health policy by engaging with regulatory bodies early, generating strong clinical and economic evidence, collaborating with stakeholders, and advocating for policies that support innovation and address affordability. Proactive efforts help companies overcome market access barriers and align with evolving healthcare priorities.
References
- Drummond, M., Sculpher, M., Claxton, K., Stoddart, G., & Torrance, G. (2015). Methods for the Economic Evaluation of Health Care Programmes (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Sorenson, C., Drummond, M., & Kanavos, P. (2008). Ensuring Value for Money in Health Care: The Role of Health Technology Assessment in the European Union. European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies.
- Garrison, L. P., & Towse, A. (2017). Value-based pricing and reimbursement in personalised healthcare: Introduction to the basic health economics of personalised medicine. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 7(3), 10-15.
- Cohen, J. P., & Felix, A. (2014). Are payers treating orphan drugs differently? Journal of Market Access & Health Policy, 2(1), 23513.
- Towse, A., Garrison, L. P., & Puig-Peiró, R. (2020). The Use of Real-World Evidence in Health Technology Assessment. Value in Health, 23(2), 137-142.
- Cook, J. P., Vernon, J. A., & Manning, R. (2011). Pharmaceutical risk-sharing agreements. Pharmacoeconomics, 29(5), 353-365.
- World Health Organization (2020). WHO Guideline on Country Pharmaceutical Pricing Policies. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- Kanavos, P., Ferrario, A., Vandoros, S., & Anderson, O. (2013). Ethical and value-based aspects of access to high-cost pharmaceuticals in the NHS. Health Economics, Policy, and Law, 8(2), 185-208.
- Wilking, N., & Jönsson, B. (2005). A Pan-European Comparison Regarding Patient Access to Cancer Drugs. Karolinska Institute and Stockholm School of Economics.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2021). Real-World Evidence. FDA.gov.

This article has been prepared with the assistance of AI and reviewed by an editor. For more details, please refer to our Terms and Conditions. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author.





